The Giant Panda - An Endangered Species
Giant Panda
- Large mammal with a distinct black and white fur pattern
- Adults weigh between 200 and 300 pounds
- Males generally are much larger than females
- Opposable thumbs, useful for them to gather bamboo for eating
- Strong jaw and large molars, useful for a bamboo diet
Meet the Giant Panda! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dqT-UlYlg1s
Species Habitat
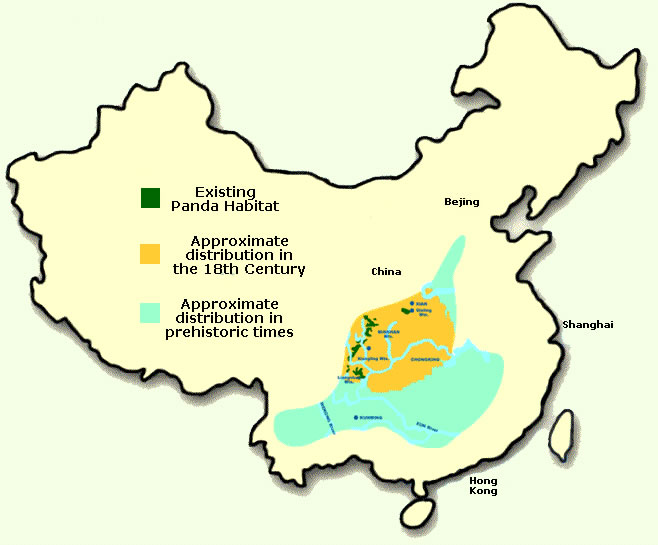
- Native to mountainous regions of central China
- Inhabit the bamboo forest of Qinling (Shaanxi Province), Minshan, Qiolai, and Liangshan (Sichuan, Gansu, and Yunnan Provinces).
- Dense vegetation and temperate climates
- Coniferous and broadleaf forests, with bamboo being the dominant plant species
- Cool and wet climate, with high rainfall and foggy conditions
Species Role in Ecosystem
The bamboo specialist, the Giant Panda, helps regulate bamboo growth by the plant being the species primary source of diet, preventing it from overgrowing which is a common issue with bamboo. The Giant Panda's feeding and movement inadvertently disperses bamboo seeds, aiding in the regeneration and diversity of the forests in which they reside. The Giant Panda's role and habitat modifications create an ideal ecosystem for other species, and due to their specific habitat requirements, their presence serve as an indicator of good health of their habitat.
Cause of Decline
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
The conversion of land for agriculture, logging, and infrastructure development has led to the loss and fragmentation of the panda's habitat. The Giant Panda's habitat is very sensitive to change, and requires very specific conditions that are unfortunately difficult to replicate artificially.
Bamboo Decline
Changes in climate patterns negatively impact bamboo forests, affecting the primary food source of Giant Pandas. Additionally, bamboo flowering, a natural phenomenon, can lead to mass die-offs of bamboo stands.
Poaching
Historically, giant pandas were hunted for their fur, resulting in a significant decline in their population. Poaching has been reduced due to conservation efforts and legal protection, however, illegal wildlife trade still remains a threat.
Why Should We Care?
The extinction would cause a significant loss of biodiversity. Ecological interactions within their habitat would be heavily disrupted and lead to cascading effects on other plant and animal species. Additionally, the loss of the Giant Panda would cause bamboo to become invasive and overgrown due to the plant being controlled through the Panda's diet.
Without doing much research, most people can recognize the cultural and symbolic significance of the Giant Panda. The species hold major cultural significance in China, deeply ingrained in local traditions, folklore and national identity. Additionally, the Giant Panda serves as an international symbol of all wildlife conservation, which is why it is important to protect this endangered species and their habitat.
Current Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts have shown positive results, as the Giant Panda was downgraded from "endangered" to "vulnerable" on the IUCN Red List in 2016. However, further efforts are important to maintain and further improve the status of the species and its habitat.
Protected Areas
Giant Panda's habitat is under protection, restrict human activities, and support the survival of the species. Efforts have been put in place to restore and reconnect fragmented parts of the Giant Panda's habitats. These efforts promote gene flow and increase the chances of successful breeding.
Legal Protection
China has national laws, such as the Wildlife Protection Law, the prohibit the hunting, killing, trading, and possession of Giant Pandas and their body. Provinces with Giant Panda populations also have additional regulations specific to the protection of pandas within their jurisdictions.
Captive Breeding
Breeding programs have helped with the reintroduction of the Giant Panda into its' natural habitat. Breeding centers focus on successful reproduction through improved environments when their natural habitats have been in poor conditions. The centers assist on raising and preparing the species for potential reintroduction into the wild.
Geographers, Geospatial tools, and Geography
Geographers use Geographic Information Systems (GIS), camera traps and telemetry to monitor the Giant Panda and their habitat. GIS software allows geographers to map and assess various factors such as habitat quality, connectivity, and the distribution of pandas and their food sources. Camera traps are remotely triggered cameras used to capture images and videos of the Giant Panda in their natural habitat. They are used to collect valuable data on their presence, behavior and population size. Telemetry systems are employed to track the Giant Pandas to help understand how the species respond to changes in their environment.
How Can You Help?
Support Conservation Organizations: Donate to reputable conservation organizations that focus on panda conservation, such as World Wild Life.
Promote Sustainable Consumer Choices: Consider the products you purchase don't contribute to deforestation and habitat destruction.
Choose Responsible Tourism: Pandas are often the source of tourism, choose responsible tourism that prioritizes the well-being of pandas and their habitats.
Reduce Carbon Footprint: Climate change will forever remain a threat to a lot of species, including the Giant Panda. Adopt sustainable practices such as energy conservation and recycling.
Spread Awareness: Educate others on the importance of the Giant Panda conservation and the hardships they face. This can be done through social media, campaigns, or public speaking.



Comments
Post a Comment